

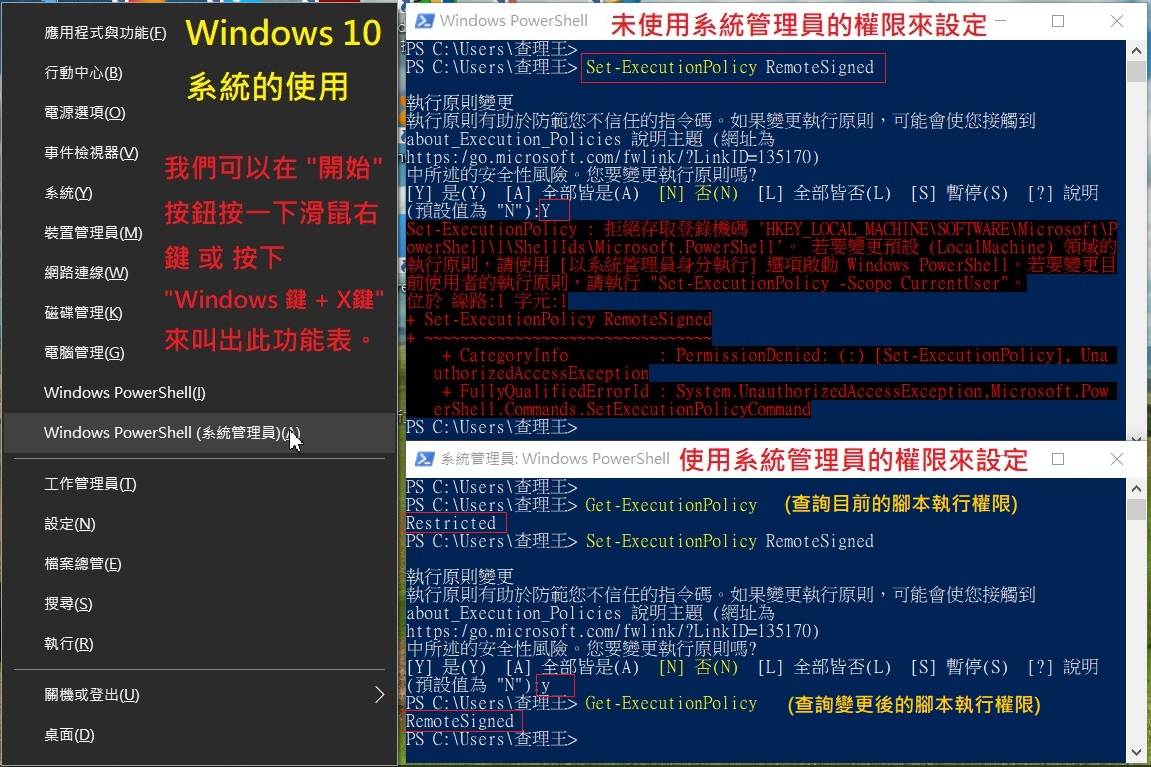
What You Will Needīefore we can start this guide, there are a few things you need to have ready: And if you do face instability, you can always reset back to defaults. Note that lower voltage may cause system instability (crashes, stutters, or freezes), but it will not damage the CPU. But, undervolting compared to overclocking is relatively safe since it effectively reduces the CPU strain on the CPU. Playing around with a CPU’s power draw in BIOS can be a scary thought for most people. Here’s a video from Optimum Tech explaining the benefits and safety of undervolting: So, undervolting for small-form-factor cases, laptops, or console-like devices can be extremely useful. In some cases, the core clock frequency can be reduced for even lower power consumption. This is done by lowering voltage requirements while maintaining the same CPU speeds. To get that temperature sweet spot, users can undervolt their CPUs. High power draw brings a couple of disadvantages: it reduces the CPU’s lifespan, increases heat output, and leads to higher electricity bills. For example, tasks like gaming or rendering require a lot of processing, so the CPU starts drawing considerably more power.ĭepending on the CPU model, strenuous tasks can lead to a power draw of up to 300W, while basic online browsing can be around 50W or less. Before we get on with the steps to undervolting a processor, it’s best that we first explain how it works and its benefits.ĬPUs use different amounts of power based on the task they are working on.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
